
Aerators are devices used to add air or oxygen to a liquid solution such as water or wastewater. They are commonly used in water treatment and wastewater treatment to help remove biological pollutants such as bacteria and microorganisms through the oxidation process. There are several different types of aerators, including mechanical, surface and submerged. They are designed to operate under different flow and pressure conditions, and can be powered by electricity, fossil fuels or renewable energy sources.
Aerators for water and effluent treatment work through different processes, depending on the type of aerator used, namely:
In general, they help to remove biological pollutants through the oxidation process, where microorganisms are exposed to oxygen and are eliminated. They can also help remove other pollutants like carbon dioxide, ammonia and other organic compounds.

Through the oxidation process, they help to remove bacteria, microorganisms and other biological pollutants from water or effluents, improving water quality.

In addition to removing biological pollutants, they can also help remove other pollutants such as carbon dioxide, ammonia and organic compounds, further improving water quality.
Many are designed to be easy to maintain and have components that can be easily replaced when necessary.

There are several types of aerators available, each designed to work under different flow and pressure conditions. This means they can be used in a variety of applications, from small water treatment plants to large industrial installations.

Some aerators use renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power, which means they have minimal environmental impact.
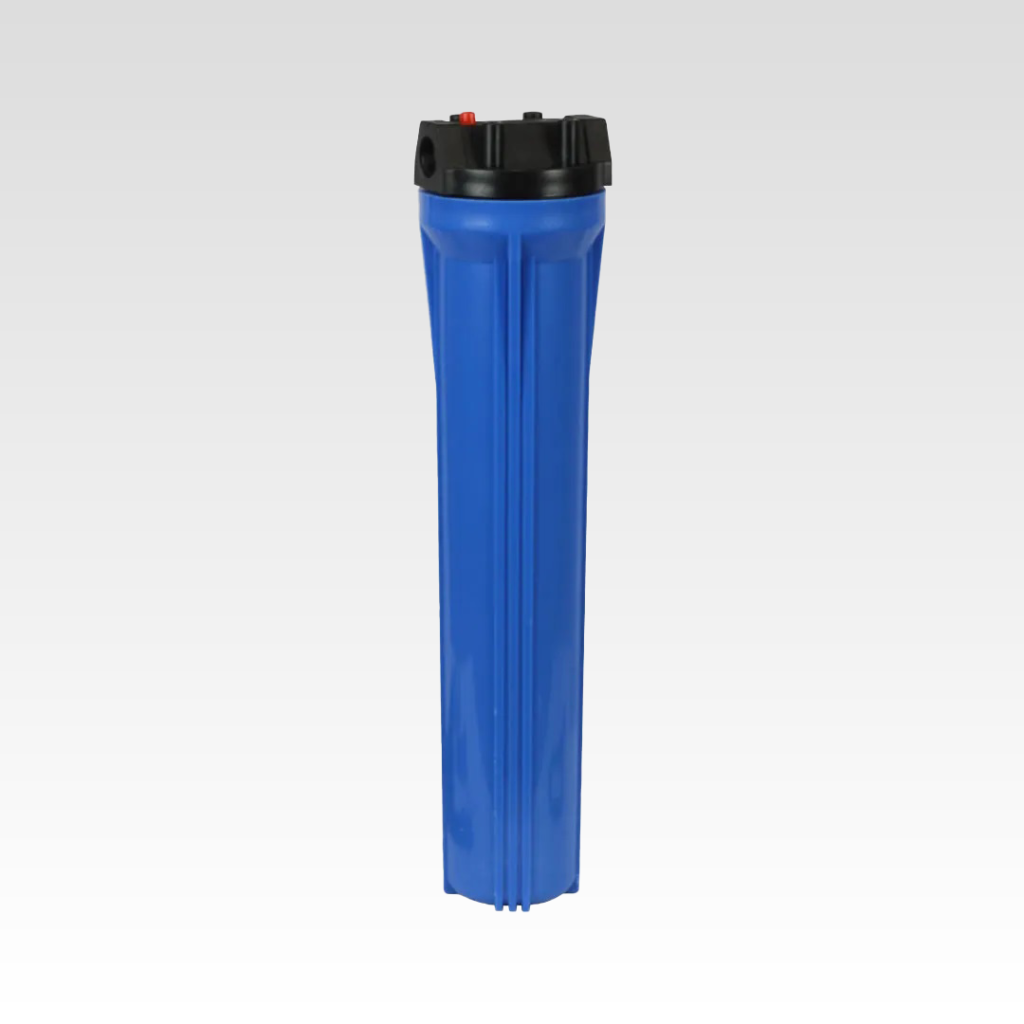

Compact polypropylene housing designed to accommodate 20-inch filter elements,...
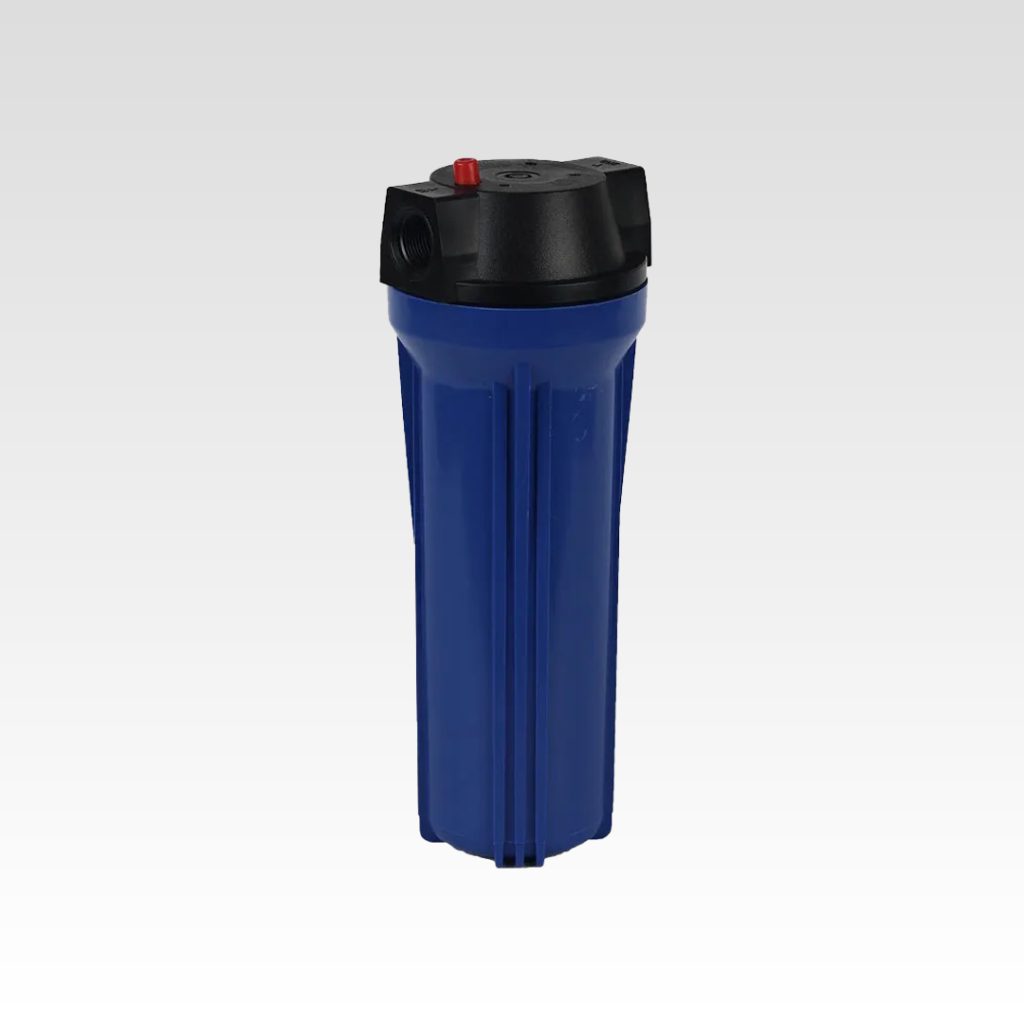

Compact polypropylene housing designed to accommodate 10-inch filter elements,...
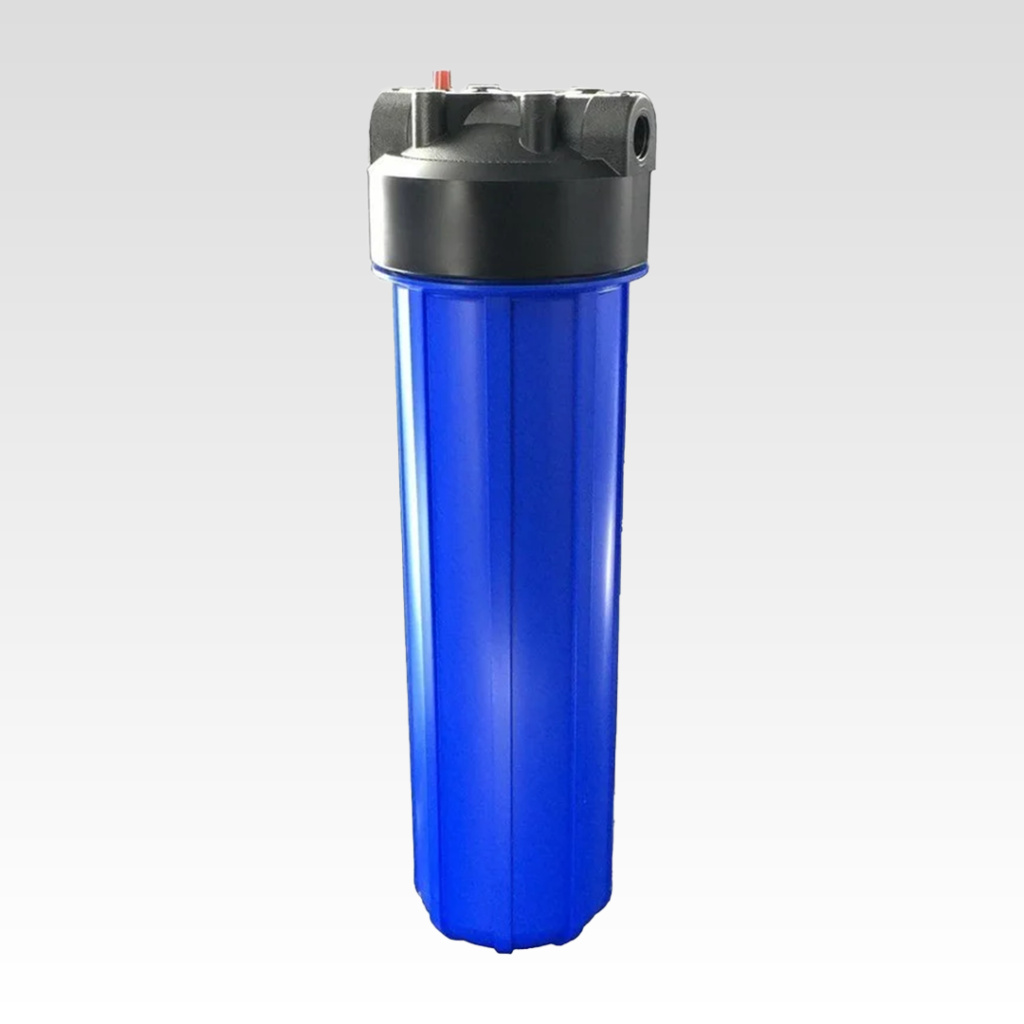

Robust polypropylene housing designed to accommodate 10-inch filter elements,...
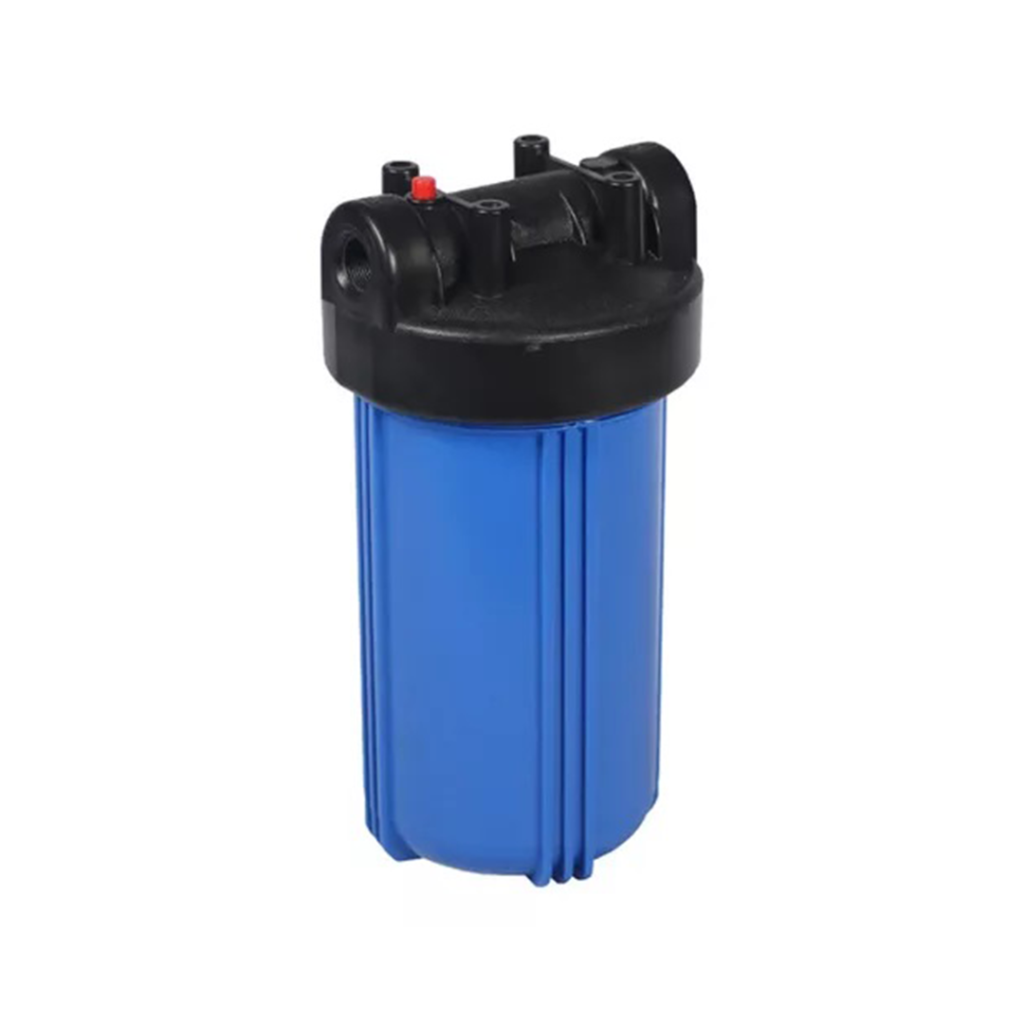

Robust polypropylene housing designed to accommodate 20-inch filter elements,...