Anaerobic Effluent Treatment is a wastewater treatment process that uses anaerobic bacteria (which do not need oxygen) to decompose the organic pollutants present in the effluent. This process can be used to treat effluents from the food, pulp and paper industries, among others, and can be followed by an aerobic treatment to remove the remaining pollutants and improve the quality of the water before being released into the environment.
EP is an effluent treatment company that plays a fundamental role in preserving the environment and in finding solutions for the management of your business. It has been working with great dedication and multiplying results for over 45 years.
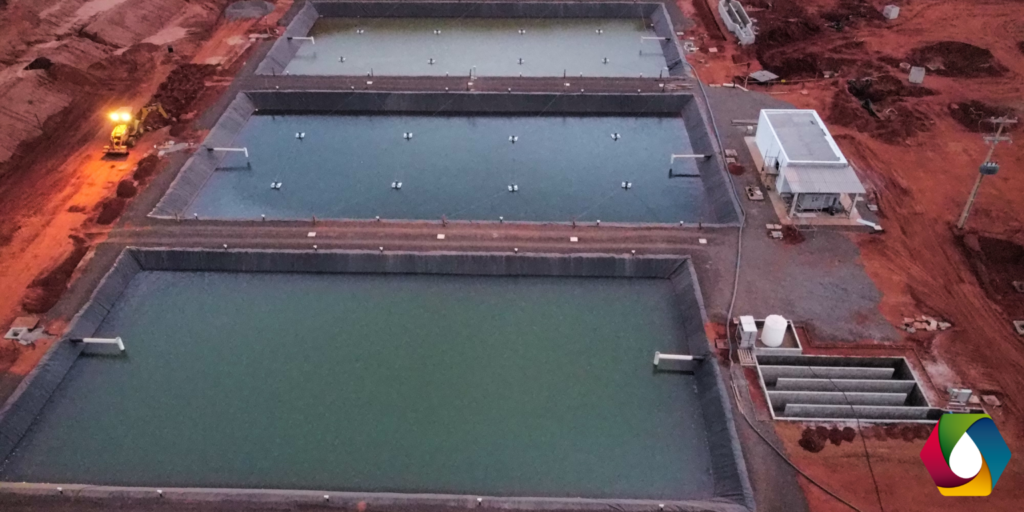

This process involves adding anaerobic bacteria to the effluent to break down the organic pollutants. During this process, bacteria convert organic pollutants into carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4) and other compounds. Methane can be collected and used as an energy source.
This process is similar to anaerobic digestion, but uses stationary tanks to keep the anaerobic bacteria and organic pollutants together for a period of time. This allows the bacteria enough time to completely break down the organic pollutants.
It is important to remember that, in some cases, the anaerobic treatment may be insufficient to completely remove the organic pollutants from the effluent and, therefore, may be followed by an additional aerobic treatment to improve the water quality.
Anaerobic treatment is effective in breaking down the organic pollutants present in effluent, reducing the pollution load before it is released into the environment.
During the treatment process, anaerobic bacteria convert organic pollutants into methane, which is a powerful and versatile biogas. This biogas can be used as a source of energy to generate electricity, heat, among others.
Anaerobic treatment is generally more economical than aerobic processes due to lower oxygen requirements and greater decomposition efficiency.
Anaerobic treatment requires less space than aerobic processes, which makes it an attractive option for industries and other facilities with limited space.
Anaerobic treatment can be used to reduce unpleasant odors that can be produced during the treatment of organic effluents.
Anaerobic wastewater treatment is widely used in various industries, including:
In general, anaerobic treatment is a more suitable option when organic matter is high and other forms of treatment are not efficient.