Generating biogas from from a biogas Treatment Treatment Treatment Plant (STP) is a sustainable way of taking advantage of the organic matter in waste, reducing energy costs and environmental impacts..
Main Steps to Generate Biogas
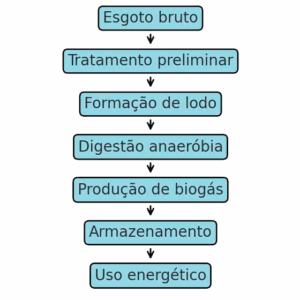
- Sludge production: During sewage treatment, the formation of biological sludge, rich residue in matter organic, which é a main materialcousin for the production of biogas.
- Anaerobic digestion: The sludge is sent to an anaerobic digester, where microorganisms degrade the organic matter without oxygen. This generates biogas and digestate.
- Collection and storage: O biogas é collected in the biodigester and stored in tanks. It can be purified to increase the concentration of methane .
- Energy use: Biogas can be used to generate generation, thermal or transformed into biomethane for use as fuel..
Common technologies in WWTPs
- UASB reactors (Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket): treat sewage from anaerobically anaerobic form and generate biogas directly.
- Closed sludge digesters: ideal for large WWTPs.
- Covered anaerobic lagoons: lower cost solution, where the tarpaulin captures the biogas.
Benefits
- Reducing electricity costs.
- Lower emission of gases greenhouse emission.
- More sustainable disposal of sludge.
- Possibility of generate revenue from carbon credits or selling ..
Points of attention
- Control required organic load and temperature to maintain efficient digestion.
- Treatment of H2S (highly corrosive).
- Assess economic viability: requires investment in biodigesters and systems systems systems.
Flowchart of the Biogas Generation Process
Biogas Production Estimates (Summary)
A biogas production depends on on the organic load of the sewage, efficiency of efficiency and operating conditions. Typical values for WWTPs are:
– ETE Small (100 m3/day): ~4 m3 of biogas/day (~84 MJ/day).
– ETE Average (1.000 m3/day): ~42 m3 of biogas/day (~840 MJ/day, equivalent a ~70 kWh/day of electricity).
These figures are conservative estimates and may vary depending on the quality of the sewage, type of digester and adoption of technologies pre–treatment or co-digestion technologies.
Operational Challenges
- Control organic organic load and stability stability.
- Need to remove gases (H2S) from biogas.
- Preventive maintenance of equipment and continuous monitoring. Complexity of operation.
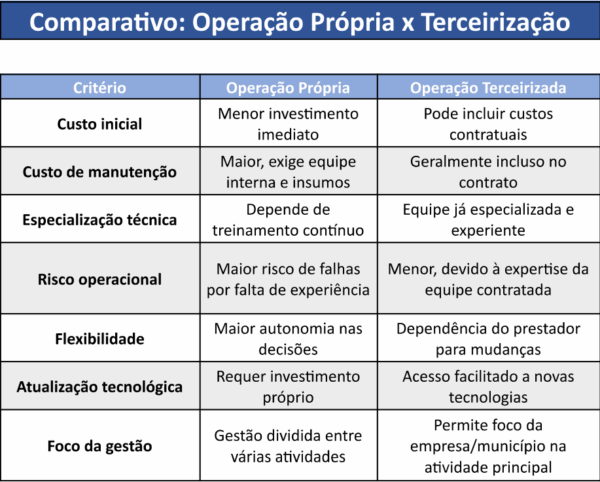
Advantages of Outsourcing Operations
- Specialized teams ensure greater efficiency and safety.
- Reducing the risk of operational failures.
- Access to up-to-date technologies and practices.
- Company/municipality focus on core business, delegating technical management.
Conclusion
The generation of biogas from Wastewater Treatment Plants represents a strategic solution for transforming an unavoidable waste product – sludge – into a renewable source of energy. By incorporating appropriate technologies and good operating practices, it is possible to reduce costs, minimize environmental impacts and increase the energy efficiency of the sanitation system. Although there are challenges related to process control, contaminant removal and initial investment, the benefits far outweigh the difficulties, especially when you rely on specialized teams or outsourced services to guarantee performance and safety.
In this way, the use of biogas is consolidated as a viable, sustainable path that is aligned with current demands for innovation and circular economy in the sanitation sector.
EP Engenharia implements this and various other technologies to develop customized solutions for clients.
Find out more about our products here.


