
Coagulation and flocculation are essential processes in the physical-chemical treatment of effluents, responsible for agglutinating suspended particles and facilitating their removal.
These processes are widely used to ensure the efficient purification of water before it is discharged or reused.
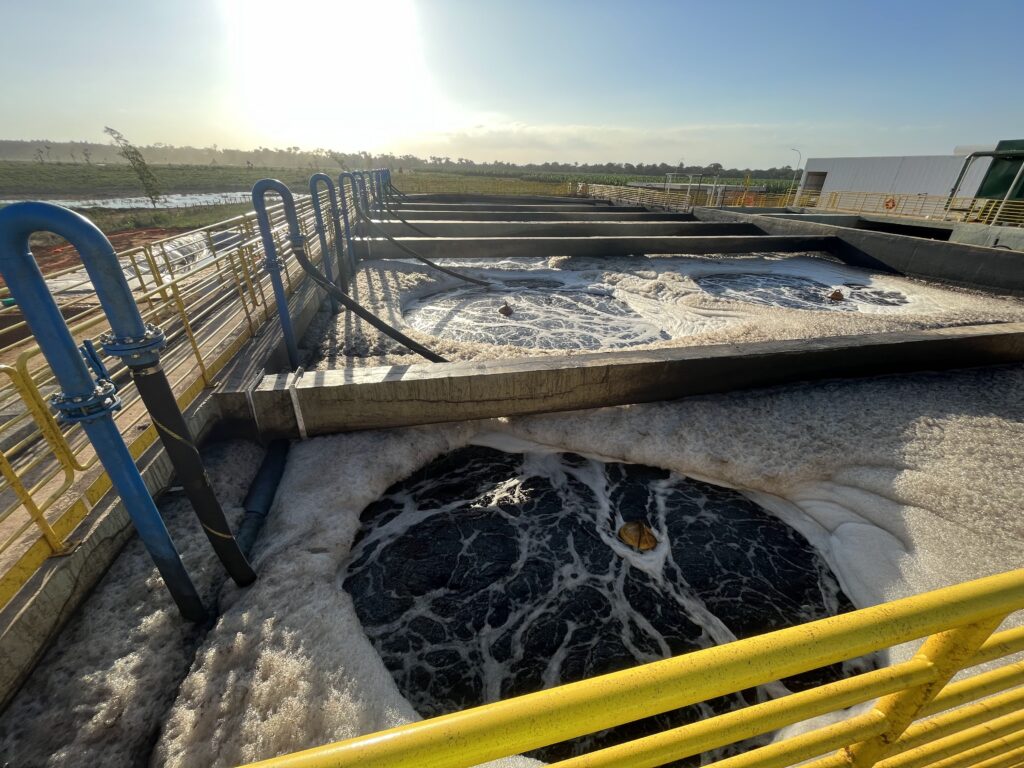



Essential for the treatment of chemical, pharmaceutical and food effluents, among others.
Used in sewage and rainwater treatment plants.
Treatment of effluents from animal husbandry and agricultural activities.
At EP, we provide high-efficiency coagulation and flocculation solutions designed to meet the specific needs of each client.
Our systems guarantee maximum efficiency and compliance with environmental standards.
Interested in finding out more about our coagulation and flocculation solutions?
Contact us today for a personalized consultation and find out how we can help improve your wastewater treatment processes.
Find out how EP can help guarantee the quality of effluent treatment for your company.

Copyright © Grupo EP | Developed by Libelle Comunicação