Surface water analysis is an essential process for assessing the quality and health of water bodies such as rivers, lakes, and reservoirs. This evaluation makes it possible to identify possible contamination and to monitor the presence of harmful substances, ensuring the safety of the water and protection of the environment.
Surface water analysis is important because surface water plays a vital role in supplying various human activities, such as consumption, agriculture, and industry. Moreover, adequate water quality is essential for the balance and survival of aquatic ecosystems.
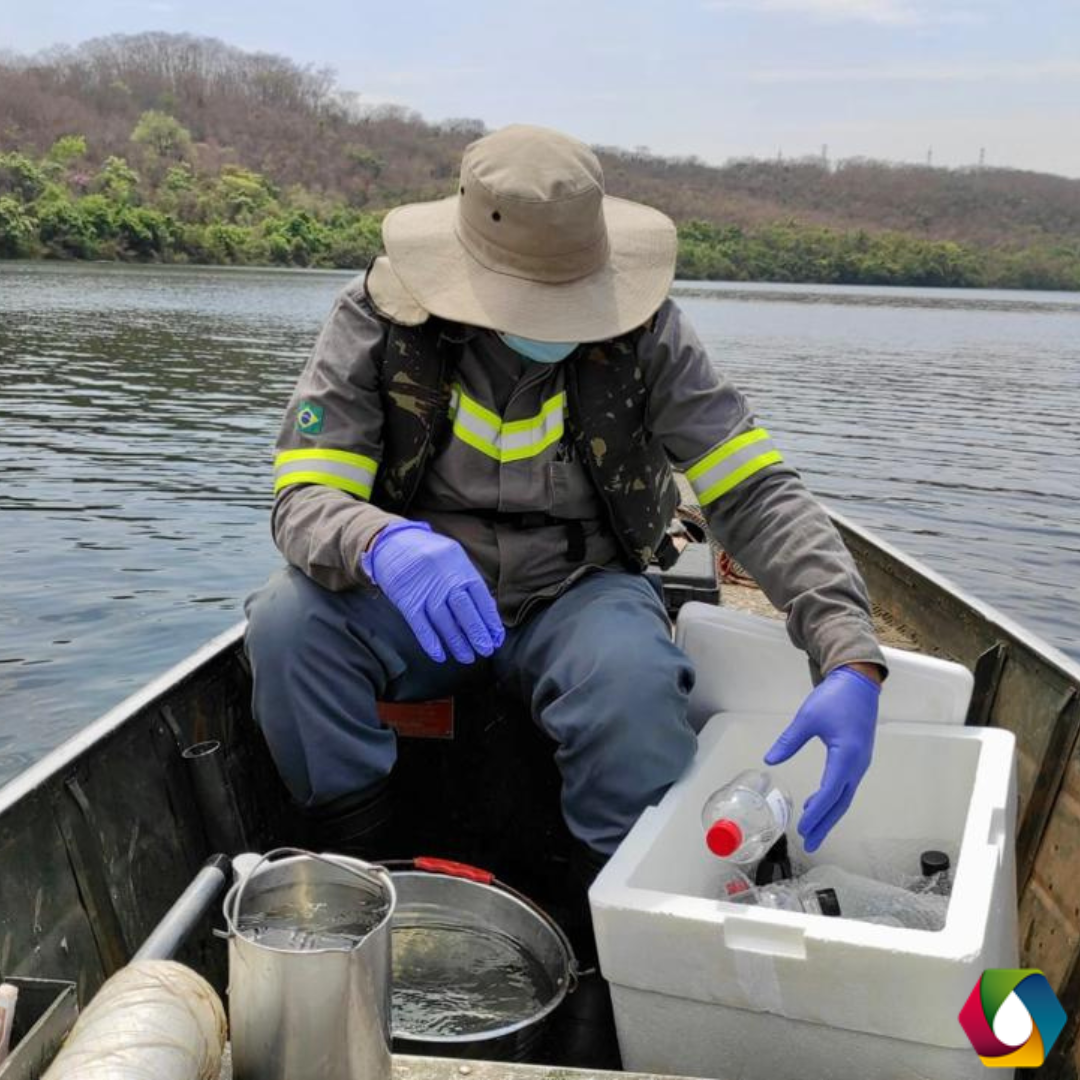
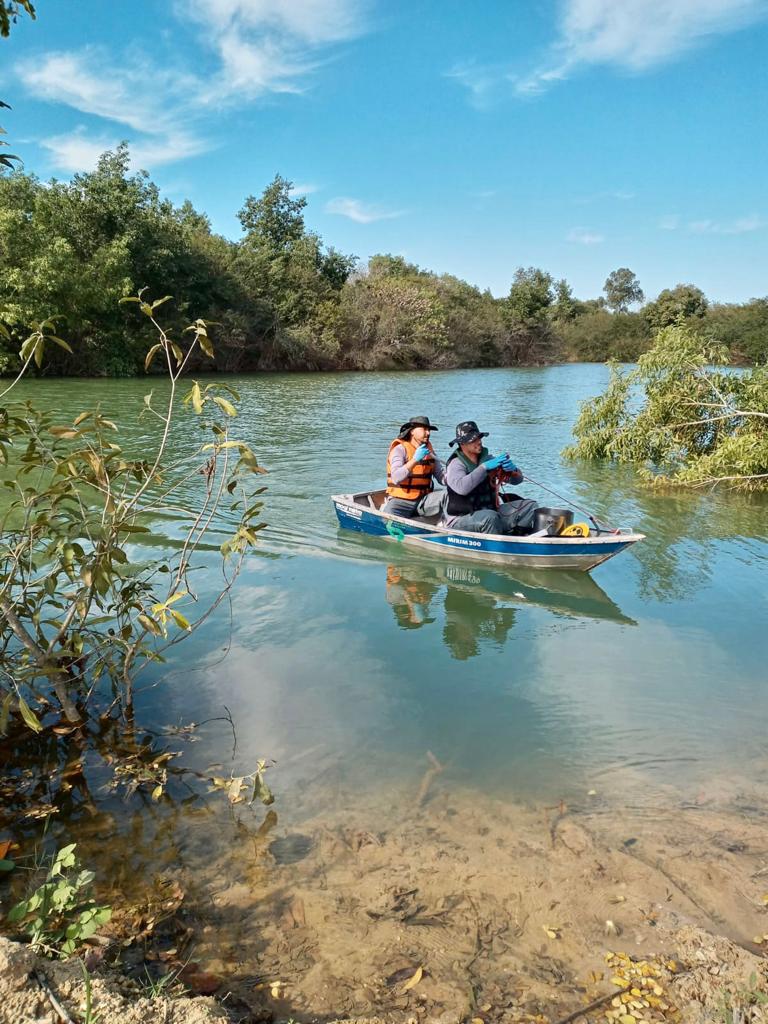
Surface water collection sites may vary depending on the purpose and context of surface water analysis. Generally, the collections are made at strategic points along water bodies, such as rivers, lakes, dams, ponds, streams, and springs.